Researchers create super-efficient Wi-Fi
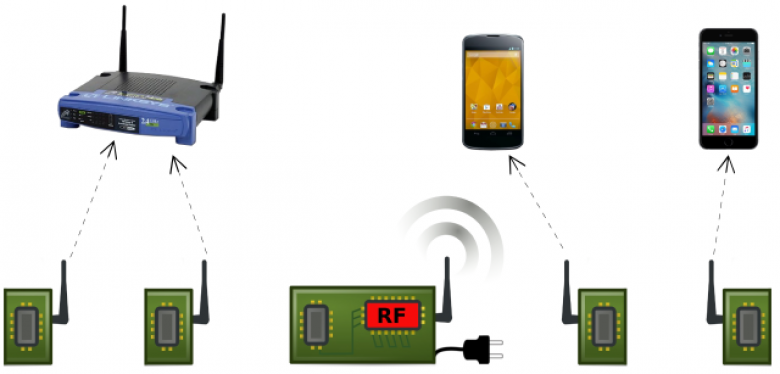
A team of computer scientists and electrical engineers from the University of Washington has developed an extremely power-efficient version of Wi-Fi wireless networking technology that consumes 10,000 times less power than the current Wi-Fi components, allowing Wi-Fi networking to be built into a much wider range of devices. The team will present a paper (PDF) with the results of their research into what they have dubbed Passive Wi-Fi at the upcoming USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation in March.
Passive Wi-Fi is, as the name suggests, partially passive—it takes in radio wave energy from an outside source and reflects that signal with its data added to it. Vamsi Talla, a UW electrical engineering doctoral student and co-author of the research, explained, "All the networking, heavy-lifting and power-consuming pieces are done by the one plugged-in device. The passive devices are only reflecting to generate the Wi-Fi packets, which is a really energy-efficient way to communicate."