Scientists discover RNA modifications in some unexpected places
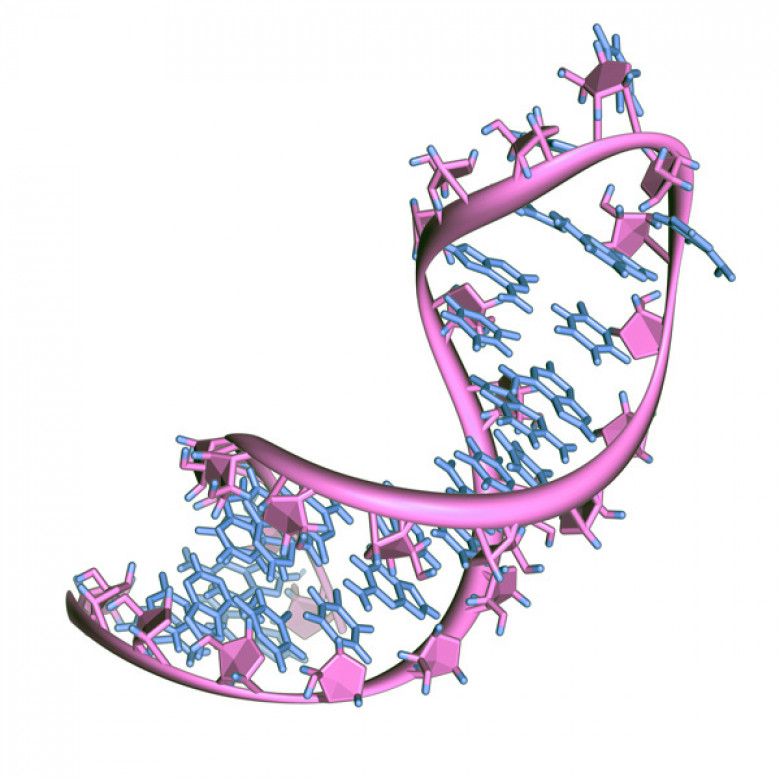
The so-called central dogma of molecular biology—that DNA makes RNA which makes protein—has long provided a simplified explanation for how genetic information is deciphered and translated in living organisms.
In reality, of course, the process is vastly more complicated than the schema first articulated nearly 60 years ago by Nobel Laureate Francis Crick, co-discoverer of the DNA's double-helix structure. For one, there are multiple types of RNA, three of which—messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—are essential for proper protein production. Moreover, RNAs that are synthesized during the process known as transcription often undergo subsequent changes, which are referred to as "post-transcriptional modifications."